Salem Witch Trials
Image: The Salem Martyr
By Thomas Slatterwhite Noble
Noble gained a reputation for his dramatic paintings of abolitionist subjects, and later turned to the Salem witch trials for another powerful moral theme. The Salem Martyr won a silver medal at the 1869 Cincinnati Industrial Exposition. A tradition in the Noble family holds that the model for this painting was a Cincinnati librarian who was a descendant of a woman who was executed in the Salem witch trials.
Mary Easty was well respected in Salem, Massachusetts in 1692. She was a kind religious woman whose dignified demeanor fit the strict Puritan mold. She was about 58 years old at the time, and was married to Isaac Easty, with whom she had seven children. They owned and lived on a large valuable farm.
The Accusation
But even Mary was not safe from the hysteria. In April 1692, she was accused of witchcraft. The accusation shocked the village. Unlike some of the other alleged witches, Mary was not a social outcast or an outspoken woman who may have offended the villagers.
The Trial
Mary was calm and respectful during her trial. Her examination followed the pattern of most in Salem: the afflicted girls had fits in the courtroom, and were speechless at times, and the magistrate advised her to confess her guilt, which he deemed proven beyond doubt by the sufferings of the girls.
“How far have you complied with Satan?” he asked.
“Sir, I never complied with him, but pray against him all my days.”
“Confess if you be guilty.”
“I will say it, if it was my last time, I am clear of this sin.”
During the trial, when Mary Easty clasped her hands together, the hands of Mary Lewis, one of the afflicted girls, were clenched and not released until Easty released her hands. When Easty inclined her head, the afflicted girls cried out that as long as her head was inclined their necks were broken.
Easty was committed to prison after her examination. For a reason not disclosed in any of the remaining records, Mary was discharged on May 18, 1692. She and her family believed she would now be safe from further accusations. They were wrong. The afflicted girls redoubled their eforts to get her back into prison.
On May 20, one of the girls, Mary Lewis, spent the entire day experiencing fits of unprecedented severity, during which time she said she was being strangled, and claimed “they will kill Easty out right.” Several of the other afflicted girls claimed that they could see the apparition of Easty afflicting her, and people came from all around to see the fits.
Second Arrest
That evening a second warrant was issued for Mary Easty’s arrest. At midnight, after experiencing two days of liberty and being reunited with her family, she was rousted from her sleep by the Marshal, torn from her husband and children, and taken back to prison where she was loaded with chains. Once she was back in prison, Mary Lewis’s fits stopped.
Second Trial
Mary Easty was tried and condemned to death on September 9. Her sister, Rebecca Nurse, had been hanged for witchcraft two months earlier. Another sister, Sarah Cloyce, had been tried, but was later released.
Before her execution, Easty wrote a letter to the judges asking that “no more innocent blood be shed.” Her letter raised sympathy and doubt in Salem Village, but could not prevent the last round of hangings. The court had long since ceased to pay any attention to anything that was said by the condemned.
The Execution
Easty and seven others – Martha Corey, Alice Parker, Ann Pudeator, Margaret Scott, Wilmot Reed, Samuel Wardwell and Mary Parker – were carted to Gallows Hill and hanged on September 22, 1692.
According to writer Robert Calef, “when she took her last farewell of her husband, children and friends, was, as is reported by them present, as serious, religious, distinct, and affectionate as could well be expressed, drawing tears from the eyes of almost all present.”
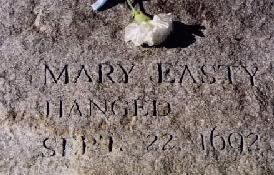
Mary Easty Commemorative Stone
Two months after the hanging, Mary Herrick gave testimony about Easty. Herrick testified that she was visited by Easty, who told her she had been put to death wrongfully and was innocent of witchcraft, and that she had come to vindicate her cause. In 1711, Easty’s family was compensated with 20 pounds from the government for her wrongful execution.
SOURCES
Mary Easty
Salem Witchcraft Trials
Salem Witch Trials – The People







So cool I just found out tonight through ancestrydna that Mary is my 9th great-grandmother on my mommas side of the family.
Me aswell! Crazy lol!
Mary’s my 12th gen great grandmother on my great grandmother’s side.
Found out a few months ago She was my 11th generation grandmother on my mothers side as well
She is also my ancestor. Hello fam!